Introduction to Stock Pots
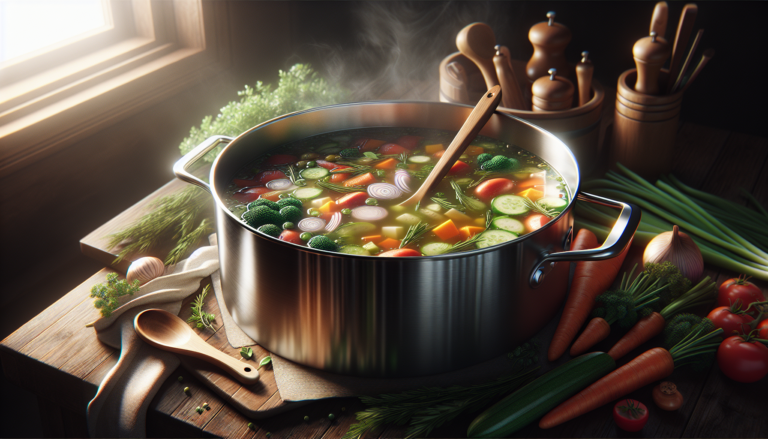
A stock pot is an essential piece of cookware in any well-equipped kitchen. This large, deep pot is designed for preparing stocks, soups, stews, and other liquid-based dishes in large quantities. Stock pots come in various sizes, typically ranging from 6 to 20 quarts or more, making them suitable for both home cooking and commercial kitchen use.
The versatility and convenience of a stock pot make it a valuable tool for any home cook or professional chef. Its size allows for cooking large batches of food, which is perfect for meal prepping, family gatherings, or hosting events. Additionally, the tall sides and heavy bottom of a stock pot promote even heat distribution and prevent burning, ensuring that your dishes come out perfectly cooked every time.
What is a Stock Pot?
A stock pot is a large, deep cooking pot with tall sides and a wide base. It is primarily used for making stocks, soups, and stews, but its versatility extends to various other cooking tasks such as boiling pasta, blanching vegetables, and even canning. Stock pots are available in different sizes, with capacities ranging from 6 to 60 quarts or more, catering to various cooking needs.
The tall sides of a stock pot allow for a greater volume of liquid to be heated, while the wide base provides even heat distribution. This design is ideal for simmering ingredients over long periods, extracting flavors, and creating rich, flavorful dishes. Stock pots often come with a tight-fitting lid, which helps to retain moisture and heat during the cooking process.
Key Features of a Stock Pot
Several key features make a stock pot an indispensable tool in the kitchen:
1. Large capacity: Stock pots are designed to hold large volumes of liquid, making them perfect for preparing big batches of soups, stews, or stocks. This feature is particularly useful for meal prepping or cooking for a crowd.
2. Tall sides: The high sides of a stock pot prevent rapid evaporation and allow for a greater depth of liquid. This design is ideal for simmering ingredients over long periods without the risk of boiling over.
3. Wide base: A wide base ensures even heat distribution, preventing hot spots and reducing the risk of burning. This feature is crucial when cooking dishes that require long simmering times.
4. Heavy-duty construction: Stock pots are typically made from sturdy materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, or enameled cast iron. These materials provide durability and efficient heat conductivity, ensuring consistent cooking results.
5. Handles: Most stock pots come with two looped handles on either side, making it easy to lift and move the pot, even when it’s full. Some models also feature a helper handle on the pot’s side for added stability during transport.
By understanding these key features, you can better appreciate the benefits of using a stock pot in your cooking and make an informed decision when choosing the right one for your needs.
Common Uses of a Stock Pot
Making Stocks and Broths
One of the primary uses of a stock pot is to prepare homemade stocks and broths. These flavorful liquids form the foundation for many soups, stews, sauces, and other dishes. To make a stock, ingredients such as bones, vegetables, herbs, and spices are simmered in water for an extended period, typically several hours. The long cooking time allows the flavors to develop and the nutrients to be extracted from the ingredients, resulting in a rich and nourishing liquid.
The tall sides and heavy bottom of a stock pot are ideal for this process, as they allow for a large volume of liquid to be heated evenly without the risk of scorching. The pot’s size also enables you to prepare large batches of stock, which can be stored in the refrigerator or freezer for future use.
Preparing Soups and Stews
Stock pots are the perfect vessel for making hearty soups and stews. The pot’s size accommodates a large volume of ingredients, while its tall sides allow for ample space for the soup or stew to simmer and develop flavors. The wide base of the stock pot ensures even heat distribution, preventing the ingredients from sticking or burning.
To make a soup or stew, you typically start by sautéing aromatic vegetables such as onions, garlic, and carrots in the stock pot. Then, you add your choice of proteins, such as meat or beans, along with stock or broth and additional vegetables. The ingredients are simmered until tender and the flavors have melded together. The result is a comforting and satisfying one-pot meal that can feed a crowd.
Boiling Pasta and Vegetables
A stock pot’s size and shape make it an excellent choice for boiling pasta or blanching vegetables. The pot’s tall sides allow for a generous amount of water to be heated, providing ample space for the pasta or vegetables to cook evenly. The wide base of the pot also ensures that the water comes to a boil quickly and maintains a consistent temperature throughout the cooking process.
When boiling pasta, it’s essential to use a pot that is large enough to accommodate the pasta’s expansion as it cooks. A stock pot’s size is perfect for this purpose, as it allows the pasta to move freely in the water, preventing it from sticking together. Similarly, when blanching vegetables, the spacious interior of a stock pot enables you to cook a large batch at once, saving time and effort.
Batch Cooking and Meal Prep
Stock pots are an excellent tool for batch cooking and meal prepping. Their large capacity allows you to prepare significant quantities of food in a single session, which can then be portioned out and stored for later use. This approach saves time and effort in the long run, as you can cook once and enjoy multiple meals throughout the week.
Some examples of dishes that are well-suited for batch cooking in a stock pot include:
– Chili
– Bolognese sauce
– Curry
– Soup
– Stew
By preparing these dishes in large batches, you can ensure that you have a variety of meals on hand, ready to be reheated and enjoyed whenever needed. The stock pot’s size and sturdy construction make it the ideal vessel for this type of cooking, as it can withstand extended cooking times and accommodate a large volume of ingredients.
Materials and Construction of Stock Pots
When choosing a stock pot, it’s essential to consider the materials and construction, as these factors can significantly impact the pot’s performance and durability. Stock pots are available in various materials, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision when selecting the right stock pot for your needs.
Stainless Steel Stock Pots
Stainless steel is a popular material for stock pots due to its durability, resistance to rust and corrosion, and easy maintenance. Stainless steel stock pots are non-reactive, meaning they won’t impart any unwanted flavors or odors into your food. They also tend to have a shiny, attractive appearance that looks great in any kitchen.
When choosing a stainless steel stock pot, look for models with a tri-ply or multi-ply construction, which features layers of stainless steel sandwiching an aluminum or copper core. This construction provides excellent heat conductivity and even heat distribution, preventing hot spots and ensuring consistent cooking results.
Aluminum Stock Pots
Aluminum is another common material for stock pots, known for its excellent heat conductivity and lightweight design. Aluminum stock pots heat up quickly and evenly, making them an efficient choice for cooking. They are also typically more affordable than stainless steel options.
However, aluminum is a reactive material, which means it can interact with acidic ingredients like tomatoes or wine, potentially affecting the flavor of your dish. To mitigate this issue, look for anodized aluminum stock pots, which have undergone an electrochemical process that creates a hard, non-reactive surface.
Enameled Cast Iron Stock Pots
Enameled cast iron stock pots offer the heat retention and distribution properties of cast iron with the added benefit of a non-reactive, easy-to-clean enamel coating. These pots are ideal for slow-cooking dishes like stews and braises, as they maintain a consistent temperature and promote even cooking.
Enameled cast iron stock pots are also attractive, with a range of color options available to suit your kitchen décor. However, they tend to be heavier and more expensive than stainless steel or aluminum alternatives.
Hard-Anodized Aluminum Stock Pots
Hard-anodized aluminum stock pots combine the benefits of aluminum with the durability and non-reactive properties of stainless steel. The hard-anodizing process creates a hard, smooth surface that is resistant to scratches, dents, and corrosion. These pots offer excellent heat conductivity and distribution, making them a reliable choice for everyday cooking.
Hard-anodized aluminum stock pots are also lightweight and easy to handle, with a dark, matte finish that hides wear and tear. They are generally more affordable than stainless steel options while providing similar performance and durability.
Choosing the Right Stock Pot
With so many stock pot options available in the market, selecting the right one for your needs can be overwhelming. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing a stock pot:
Size and Capacity
Stock pots come in various sizes, typically ranging from 6 to 60 quarts or more. When choosing a size, consider the type of cooking you’ll be doing and the number of people you typically cook for. If you frequently prepare large batches of soups, stews, or stocks, or if you often cook for a crowd, a larger stock pot (12 quarts or more) may be a good choice. For everyday cooking or smaller households, a 6 to 8-quart stock pot should suffice.
Shape and Structure
Look for a stock pot with tall sides and a wide base. The tall sides help to prevent rapid evaporation and allow for a greater depth of liquid, while the wide base ensures even heat distribution and prevents burning. Some stock pots also feature a slightly flared rim, which makes pouring easier and less messy.
Handle Design and Comfort
A stock pot’s handles should be sturdy, heat-resistant, and comfortable to grip. Look for pots with two large, looped handles on either side, which provide a secure grip and make it easy to lift and move the pot, even when it’s full. Some stock pots also feature a helper handle on the pot’s side for added stability during transport.
Heat Conductivity and Distribution
Consider the material and construction of the stock pot, as these factors significantly impact its heat conductivity and distribution. Stainless steel pots with tri-ply or multi-ply construction, featuring layers of stainless steel with an aluminum or copper core, provide excellent heat conductivity and even heat distribution. Aluminum and hard-anodized aluminum pots also offer good heat conductivity, while enameled cast iron pots excel at heat retention and distribution.
By taking these factors into account, you can choose a stock pot that best suits your cooking needs, preferences, and budget.
Caring for Your Stock Pot
To ensure that your stock pot remains in excellent condition and performs optimally for years to come, it’s essential to follow proper care and maintenance guidelines. Here are some tips for caring for your stock pot:
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
– Always allow your stock pot to cool before cleaning to prevent warping or damage to the pot’s surface.
– Hand-wash your stock pot with hot, soapy water and a soft sponge or cloth. Avoid using abrasive scrubbers or steel wool, as these can scratch the pot’s surface.
– For stubborn, stuck-on food residue, fill the pot with hot, soapy water and let it soak for a few hours before cleaning.
– Dry your stock pot thoroughly after washing to prevent water spots and rust formation, particularly on stainless steel pots.
– Store your stock pot in a dry, cool place to prevent damage and ensure longevity.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
– Never place a hot stock pot under cold running water, as this can cause warping or damage to the pot’s surface.
– Avoid using metal utensils that can scratch the pot’s interior, especially on non-stick or enameled surfaces. Opt for wooden, silicone, or heat-resistant plastic utensils instead.
– Do not use your stock pot for dry cooking methods like searing or sautéing, as the high heat can damage the pot’s surface and cause warping.
– Avoid storing food in your stock pot for extended periods, as this can lead to staining or lingering odors.
– Never place your stock pot in the dishwasher, as the harsh detergents and high temperatures can damage the pot’s surface and cause discoloration.
By following these care and maintenance tips and avoiding common mistakes, you can keep your stock pot in excellent condition, ensuring that it remains a reliable and long-lasting tool in your kitchen.
Popular Stock Pot Recipes
A stock pot’s versatility makes it an essential tool for preparing a wide range of delicious recipes. Here are some popular dishes that showcase the many uses of a stock pot:
Easy Spaghetti
Ingredients:
– 1 pound spaghetti
– Salt
Instructions:
1. Fill a large stock pot with water and bring it to a boil over high heat.
2. Add a generous amount of salt to the water, then add the spaghetti.
3. Cook the spaghetti according to the package instructions until al dente, stirring occasionally.
4. Drain the spaghetti and serve with your favorite sauce.
Chicken and Vegetable Stew
Ingredients:
– 1 tablespoon olive oil
– 1 onion, diced
– 2 carrots, sliced
– 2 celery stalks, sliced
– 4 garlic cloves, minced
– 1 pound boneless, skinless chicken breast, cut into 1-inch pieces
– 1 teaspoon dried oregano
– Salt and pepper, to taste
– 1 (28-ounce) can diced tomatoes
– 4 cups chicken broth
– 1 (15-ounce) can kidney beans, drained and rinsed
Instructions:
1. Heat the olive oil in a large stock pot over medium heat.
2. Add the onion, carrots, celery, and garlic, and cook until softened, about 5 minutes.
3. Add the chicken, oregano, salt, and pepper, and cook until the chicken is no longer pink.
4. Add the diced tomatoes, chicken broth, and kidney beans, and bring to a simmer.
5. Cook for 20-25 minutes, or until the vegetables are tender and the flavors have melded.
6. Serve hot, garnished with fresh herbs, if desired.
Chicken and Rice Soup
Ingredients:
– 1 tablespoon olive oil
– 1 onion, diced
– 2 carrots, sliced
– 2 celery stalks, sliced
– 4 garlic cloves, minced
– 8 cups chicken broth
– 1 cup long-grain white rice
– 2 boneless, skinless chicken breasts, cooked and shredded
– 1 teaspoon dried oregano
– Salt and pepper, to taste
Instructions:
1. Heat the olive oil in a large stock pot over medium heat.
2. Add the onion, carrots, celery, and garlic, and cook until softened, about 5 minutes.
3. Add the chicken broth, rice, shredded chicken, oregano, salt, and pepper, and bring to a boil.
4. Reduce the heat to low and simmer for 20-25 minutes, or until the rice is tender.
5. Serve hot, garnished with fresh herbs, if desired.
Homemade Vegetable Broth
Ingredients:
– 1 onion, quartered
– 2 carrots, cut into chunks
– 2 celery stalks, cut into chunks
– 4 garlic cloves, whole
– 1 bay leaf
– 1 teaspoon whole black peppercorns
– 1 teaspoon dried thyme
– 8 cups water
Instructions:
1. Place all the ingredients in a large stock pot and bring to a boil over high heat.
2. Reduce the heat to low and simmer for 1-2 hours, or until the vegetables are very soft and the broth is flavorful.
3. Strain the broth through a fine-mesh sieve and discard the solids.
4. Use the broth immediately, or allow it to cool before storing in the refrigerator or freezer for later use.
Corn on the Cob
Ingredients:
– 6-8 ears of fresh corn, husked
– Salt
Instructions:
1. Fill a large stock pot with water and bring it to a boil over high heat.
2. Add a generous amount of salt to the water, then carefully add the corn.
3. Cook the corn for 3-5 minutes, or until tender.
4. Remove the corn from the pot using tongs and serve hot with butter, if desired.
Conclusion
A stock pot is an incredibly versatile and essential tool in any well-equipped kitchen. Its large capacity, tall sides, and wide base make it ideal for preparing a wide range of dishes, from stocks and broths to soups, stews, and more. By understanding the key features and benefits of a stock pot, as well as the various materials and construction options available, you can choose the perfect pot for your cooking needs.
Proper care and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of your stock pot. By following the cleaning and maintenance tips outlined in this article and avoiding common mistakes, you can keep your stock pot in excellent condition for years to come.
With the help of a stock pot, you can prepare a variety of delicious and comforting recipes, such as easy spaghetti, chicken and vegetable stew, chicken and rice soup, homemade vegetable broth, and corn on the cob. These recipes showcase the versatility and convenience of using a stock pot in your everyday cooking.
Investing in a high-quality stock pot is a wise decision for any home cook or professional chef. By having this essential tool in your kitchen arsenal, you’ll be well-equipped to create flavorful, hearty, and satisfying meals that will delight your family and friends for years to come.
See also:
- Who Owns the Most Apple Stock? Discover the Top Shareholders
- What Is a Stock Cooperative? Understanding the Basics and Benefits
- What is the major difference between a stock company and a mutual company?
- What Do Individual Shareholders Gain When They Buy Shares of a Company’s Stock?
- Why Shopify Stock Is Down Today: Key Insights and Analysis